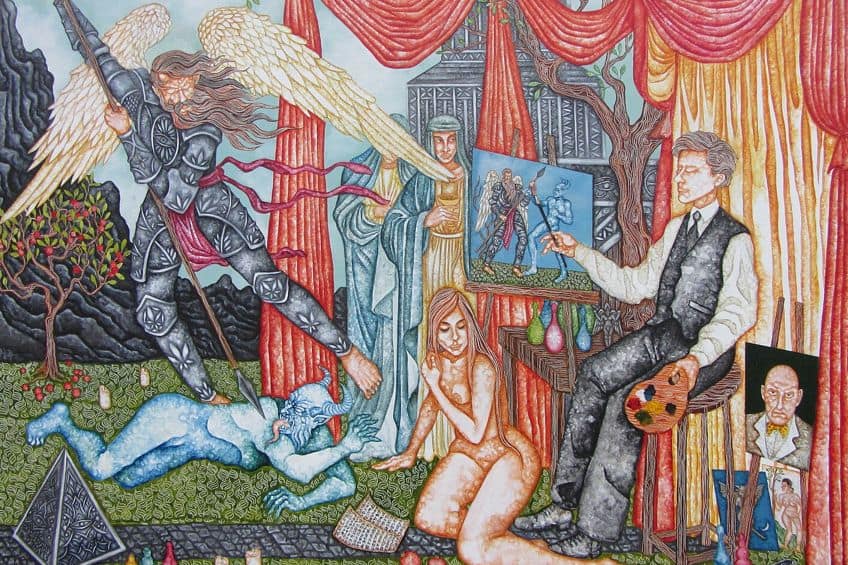
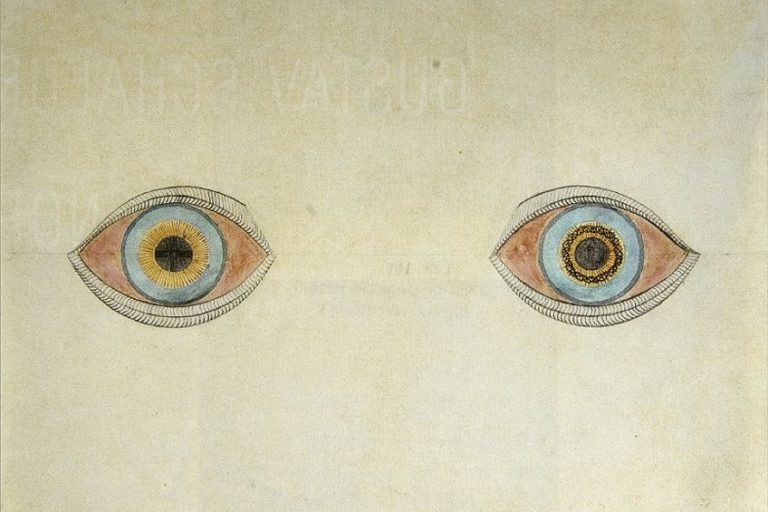
Esoteric Art – The World of Mystery and Symbolism
Welcome to the enigmatic world of esoteric art, where mysteries abound and symbols speak volumes. Esoteric art invites us to journey beyond the canvas, delving into the hidden realms of the mind and spirit. It’s a realm where alchemy meets symbolism, where the mundane transforms into the magical, and where every stroke holds a secret waiting to be deciphered. Join us as we unravel the esoteric tapestry of artistic expression, where each masterpiece is a portal to a universe of hidden meanings and boundless imagination!
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Esoteric art intertwines artistic creativity with mystical and hidden subjects.
- It stems from historical practices and evolves with cultural influences across time.
- The art form impacts contemporary culture by offering introspective and symbolic content.
What Is Esoteric Art?
Esoteric art represents a confluence of hidden knowledge and artistic expression that has pervaded much of Western cultural history. This form of art typically engages with mystic, occult, or secretive themes that are often understood by a niche audience rather than the general public. It draws upon symbolic languages and arcane philosophies ranging from alchemy to astrology, often with the intention of communicating deeper truths or portraying the ineffable aspects of human experience.
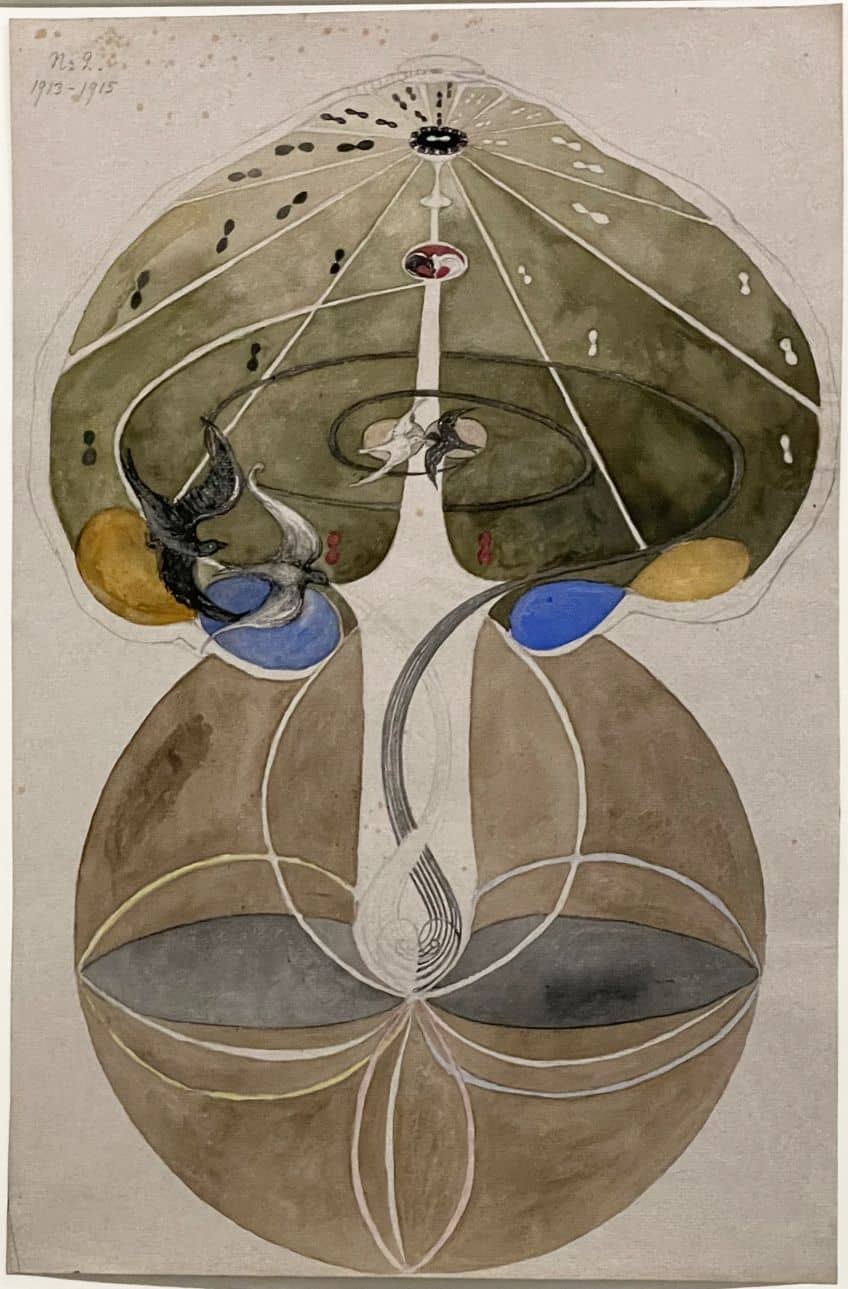
The origins of esoteric art are as varied as the disciplines it encompasses, with traces found in the rich tapestries of theosophy, gnosticism, hermeticism, and witchcraft. Over centuries, this form of art has evolved, incorporating both traditional and avant-garde elements, thereby weaving a complex historical narrative that intersects with both religion and metaphysics. Artists within this tradition have sought to use their work as a vehicle for personal and collective transformation, infusing it with symbolic meanings that provide insight into the mystical undercurrents of existence. The manifestation of esoteric themes in art has been persistent, quietly influencing contemporary culture and providing a means through which spiritual and occult practices can be explored and revered.
These artworks often serve as catalysts for reflection, inviting viewers to encounter and interpret the multilayered symbols and narratives embedded within.
Characteristics of Esoteric Art
Esoteric art is an artistic genre that communicates beyond the conventional visual elements of color, form, and composition. It seeks to convey hidden meanings or knowledge that is not immediately evident to the uninitiated observer. These works are often infused with spiritual, mystical, or occult themes, providing a visual narrative that typically requires interpretive insight to decode.
- Historical context: It spans various cultures and historical periods, often reflecting the mystical beliefs and practices of the time.
- Visual symbols: Esoteric artworks utilize a range of symbols and motifs understood within a cultural or initiatory context.
- Intended audience: The nuances embedded within esoteric art are intended for those versed in the relevant symbolic language or tradition.
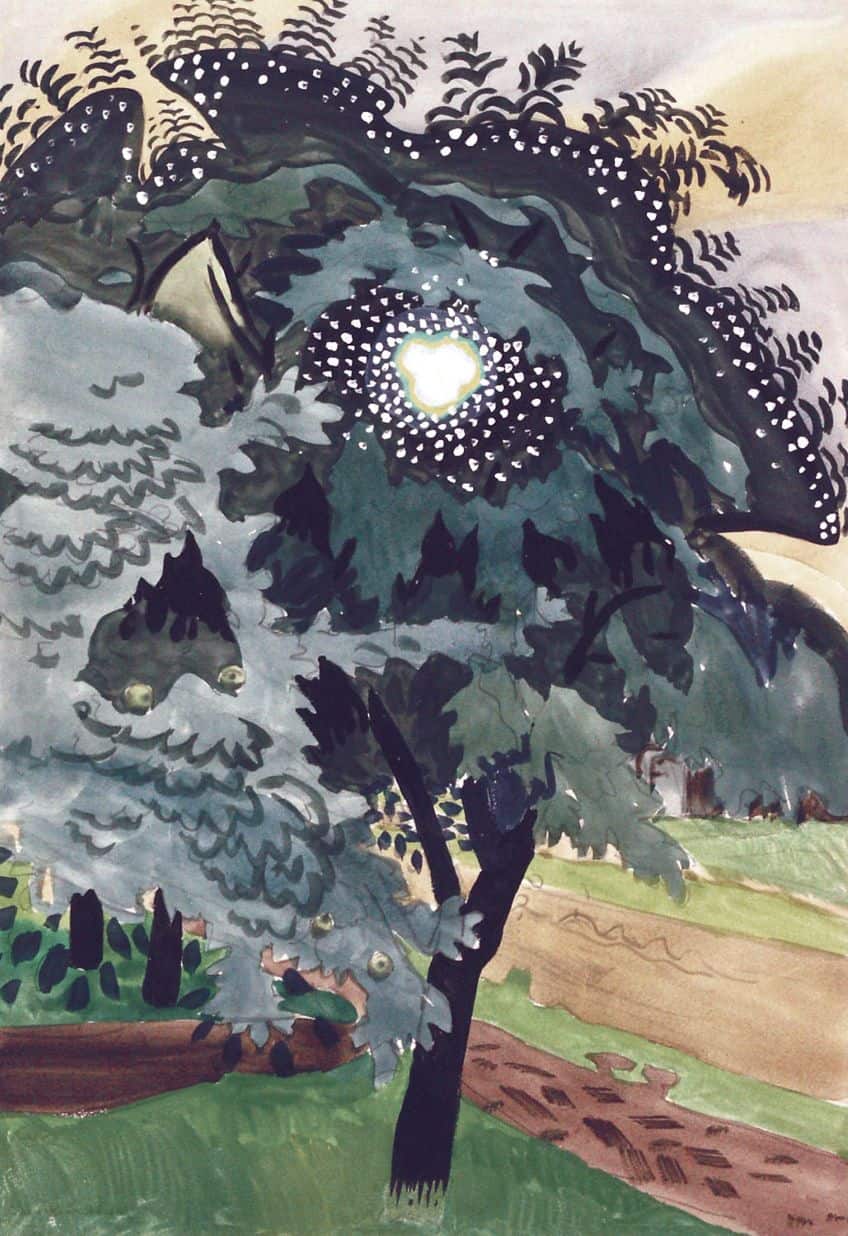

Esoteric art is multidimensional, engaging viewers in a deeper intellectual and spiritual dialogue. To appreciate its layers of meaning, one may need knowledge of the esoteric systems it portrays, such as alchemy, astrology, or other metaphysical ideologies. Artists in this genre often aim to transcend the material plane, offering a transformative experience through their works. Surrealist artists like Madeline von Foerster, who draw upon alchemy and folklore, are modern exemplars of this tradition.
Esoteric art remains a compelling avenue where the visible meets the invisible, and the profound complexities of human consciousness are explored.
Origins and Evolution of Esoteric Art
Esoteric art traces back to ancient practices where symbolism and rituals played a crucial role in conveying profound spiritual and arcane knowledge. It has evolved through various historical chapters, each adding layers to its complexity and depth.
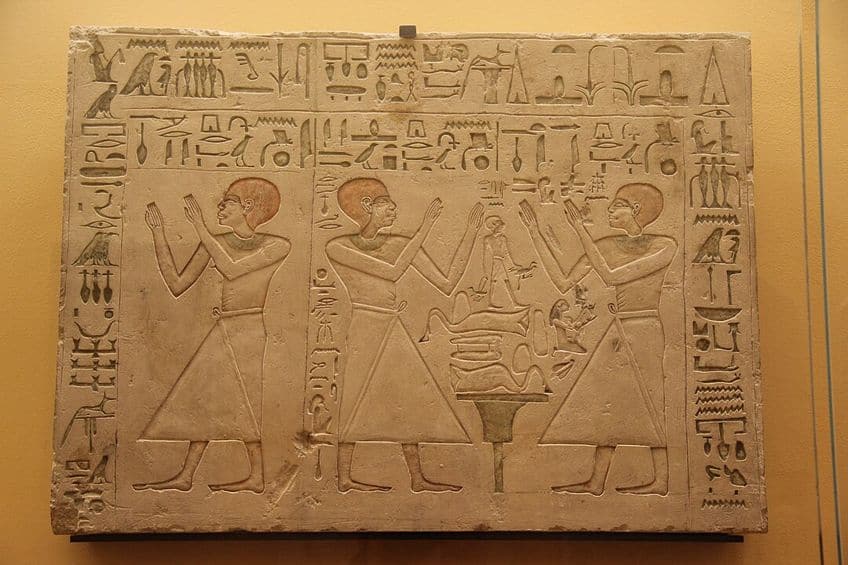
Ancient Esoteric Traditions
Ancient civilizations such as Egypt and Greece used symbols and hieroglyphs as a means to impart esoteric knowledge. In Egypt, temple adornments and funerary art were not just decorative but encoded with information understood only by the initiated.
Similarly, in Greece, esoteric beliefs were embedded in mythology and philosophy, with schools like Pythagoreanism and Platonism hinting at deeper truths through numerical and geometrical symbolism.
- Egypt: Hieroglyphs with multi-layered meanings.
- Greece: Mythological and philosophical symbols.
Renaissance and Early Modern Influences
The Renaissance period marked a resurgence in esoteric interest, with hermeticism, kabbalah, and alchemy influencing the art of the time. Alchemical symbols began to appear in paintings, containing secret knowledge about transformation and the divine. The kabbalistic Tree of Life and other mystical diagrams were integrated into the works of art to convey a deeper, often hidden, understanding of the universe.
- Hermeticism: Integration of alchemical symbols.
- Kabbalah: Mystical diagrams in art.
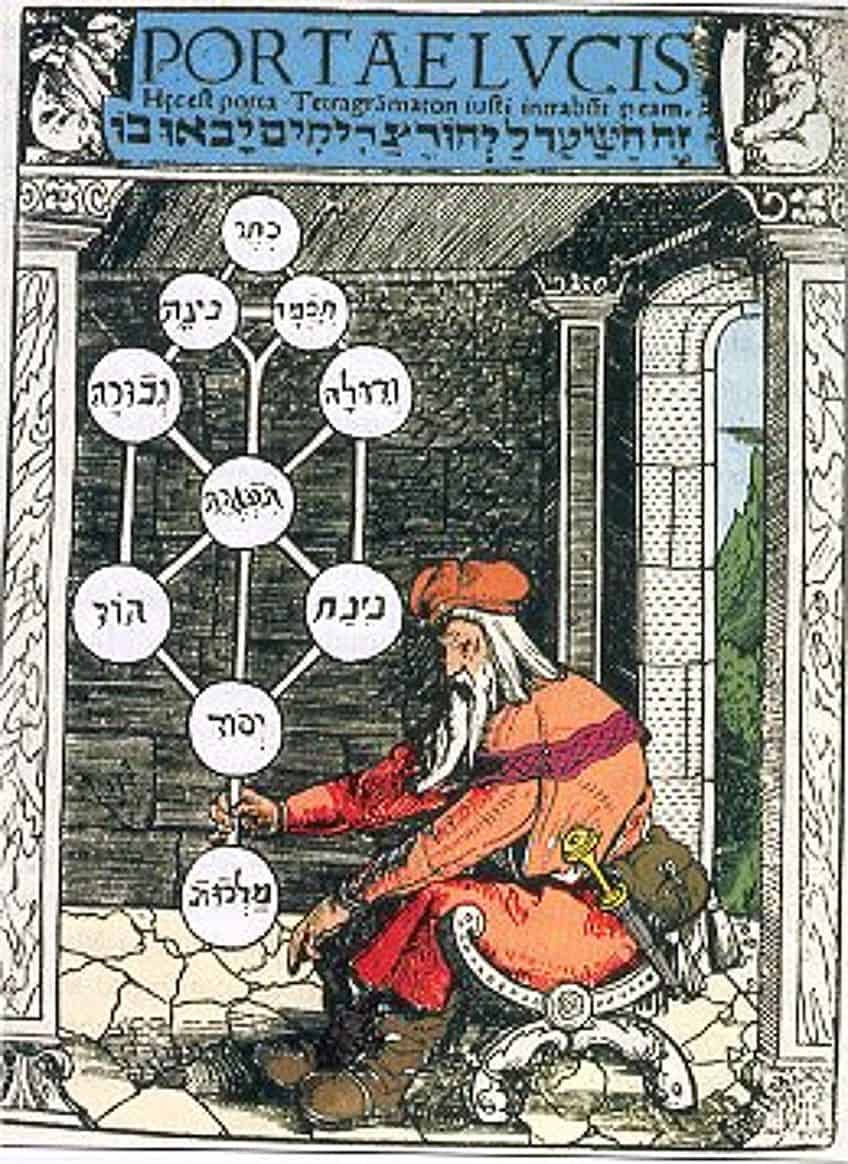
Rise in Western Esotericism
As esotericism moved through the Western world, new movements and societies emerged, each contributing to the esoteric art canon. Rosicrucianism and Freemasonry utilized intricate symbols in their iconography, Theosophical Society’s art was inspired by spiritual and mystical visions, and artistic representations of witchcraft often included layers of esoteric symbolism. This period saw a blend of art, occultism, and spirituality manifesting in unique and complex ways.
- Rosicrucianism and freemasonry: Symbol-laden iconography.
- Theosophical society: Visionary art linked with spirituality.
- Witchcraft: Symbolism in depictions of the arcane.
Esoteric art continues to adapt and merge with contemporary streams of thought, maintaining its cryptic allure and the promise of hidden truths to those who know where to look.
Symbolism and Metaphor in Esoteric Art
Esoteric art harnesses a rich vocabulary of symbols and metaphors, providing a window into the profound and oft-hidden meanings embedded within the artwork.
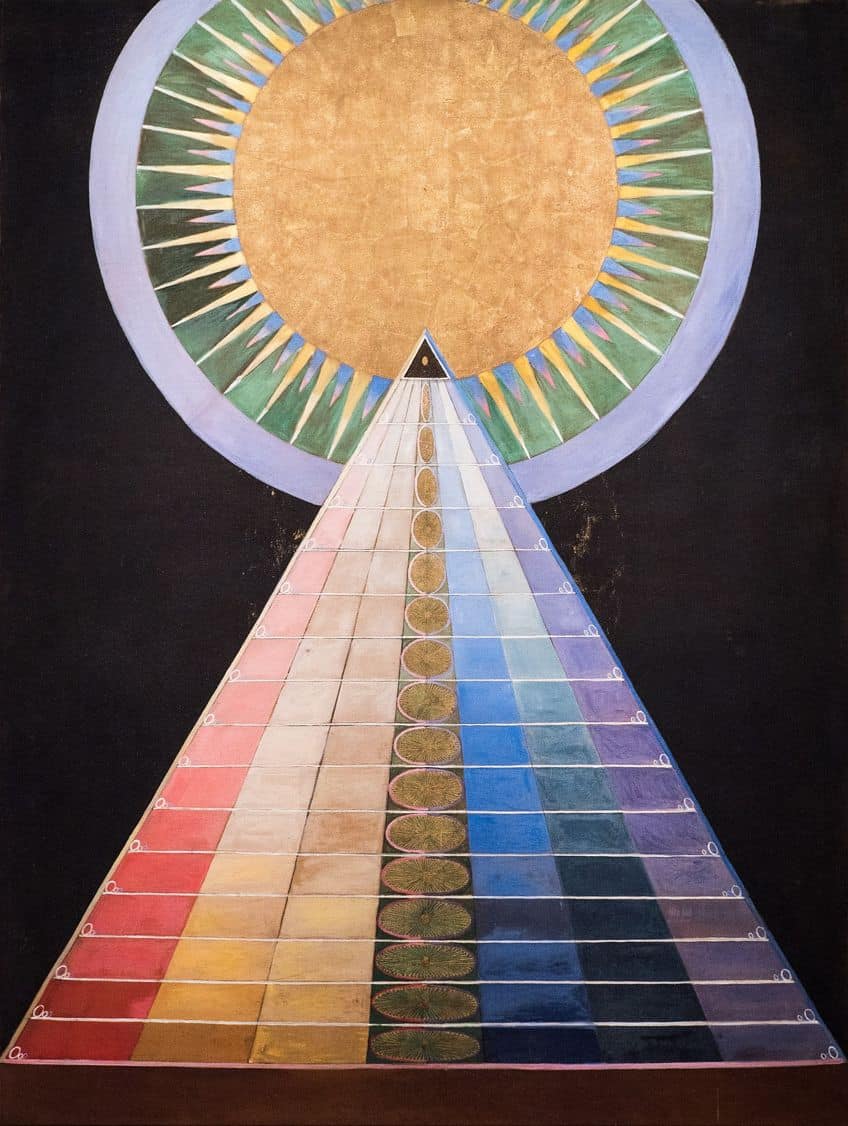

Interpreting Esoteric Symbols
Esoteric art is replete with symbols that often require specialized knowledge to interpret. Each symbol serves as a key to unlocking deeper significance that transcends the obvious. For instance, mandalas in esoteric art are not just aesthetic geometric patterns; they represent the universe and are symbols of unity and harmony. Deities and planets frequently appear in esoteric artworks, each embodying layers of cosmic and philosophical essence.
The sun, a universal esoteric symbol, signifies life-giving energy and divine presence.
Metaphysical Elements and Imagery
Metaphysical imagery, such as representations of psychic or spiritual states, imbues esoteric art with a sense of the transcendent. The use of metaphor is paramount, where tangible elements stand in for intangible concepts. Often, esoteric artwork will depict scenes or entities that are charged with energetic significance, whether through depictions of ritual, myth, or symbolic narratives. The artwork acts as a visual metaphor for a reality that lies beyond the physical or immediately observable world.
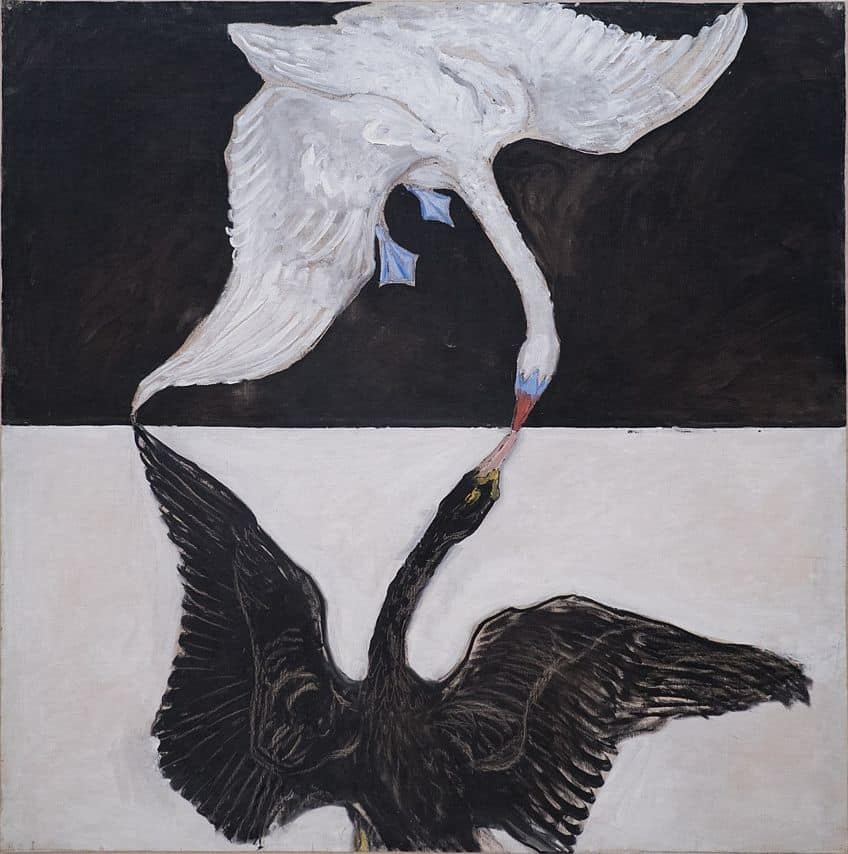

The Use of Geometry and Color
Sacred geometry and color are foundational components in esoteric art, serving as visual anchors for metaphysical concepts. Geometric shapes like circles, triangles, and squares are employed to represent concepts such as eternity, trinity, and stability. Sacred geometry is the belief that certain geometric shapes and proportions possess divine significance. The use of specific colors also carries weight in esoteric art. Colors are not chosen at random but are intent upon conveying a particular quality of energy or an attribute of the subject portrayed. For example, blue might signify depth and wisdom, whereas red could denote passion or vitality.
The precise use of geometry and color in esoteric artworks is deliberate, aiming to evoke certain states of consciousness within the viewer.
Expression of the Occult and Mystical
Artistic expression in esoteric art provides a unique lens through which the mystical and the occult are envisioned and interpreted, capturing themes of otherworldliness and the exploration of esoteric knowledge.

Occult and Mystical Themes
Esoteric art often revolves around occult and mystical themes, which are represented through various symbols, imagery, and narratives. These themes delve into the knowledge of the hidden or the supernatural, including the realms of gnosis and the Western mystery tradition. Occult themes might be illustrated through the representation of demons or arcane rituals.
In contrast, mystical elements may focus on visions, spiritual transcendence, or the manifestation of the ethereal in the material world.
Artistic Representation of the Otherworldly
The ability to depict realms beyond the ordinary experience is key to esoteric art. Artists may use a combination of surreal landscapes, abstract forms, or symbolic imagery to convey an otherworldly atmosphere. Such representations might include mediums in a trance, or ritualistic activities that suggest communication with spiritual entities. The portrayal of these unseen dimensions provides a visual bridge between the tangible world and the occultist insights that lie just beyond human perception.

Esoteric Practices and Artistic Creation
The process of creating esoteric art itself is often viewed as an esoteric practice. This can encompass the incorporation of ritualistic methods, where the act of creating art is imbued with ceremonial significance. The intention is to achieve a sort of mysticism within the creative process, ultimately instilling the artwork with a sense of the arcane.
Artists may interpret their engagement with esoteric practices as a path to enlightenment, articulating an inner quest for occult knowledge and wisdom through their creative endeavors.
Impact and Influence on Contemporary Culture
The integration of esoteric art into the fabric of contemporary culture has been reflected through various mediums ranging from visual art to literature, influencing both popular culture and the spiritual landscape.

Mainstreaming of Esoteric Elements
Esoteric art has been increasingly embraced in popular culture, often presenting ancient mystical symbols and practices within contemporary artistic expressions. Highly influential artists like Wassily Kandinsky have been inspired by these esoteric traditions, planting the seeds for modern art movements.
As esoteric themes cross into the mainstream, they alter the perception of spiritual imagery, making it more prevalent and accessible in visual art.
Modern Media and Esoteric Art
Esoteric themes have found a firm place in modern media, with representations proliferating through TV, music, and literature. Programs that explore themes like modern Paganism and Wicca resonate with audiences, becoming part of the collective conversation. Music that incorporates esoteric and mystical elements demonstrates the adaptability of these themes across various genres, influencing both sound and visual aesthetics in music videos.

Esoteric Art Today
In present times, the New Age phenomenon has further popularized esotericism, making its art more accessible. In the current art landscape, both artists and consumers show a penchant for works that encapsulate esoteric and spiritual themes, often blending classical motifs with modern techniques. This contemporary esoteric art movement is evidence of a broad cultural shift that embraces the mystical and the occult, not just as niche elements but as integral aspects of the art world.
As we conclude our exploration into the captivating realm of esoteric art, one thing becomes abundantly clear: the journey is as profound as the destination. Through the arcane symbols, mystical motifs, and hidden narratives, esoteric art beckons us to contemplate the depths of our own consciousness and the mysteries of the universe. It challenges us to expand our perception, to question the known, and to embrace the ineffable. In this dance between the seen and the unseen, the ordinary and the extraordinary, we find not just art, but a pathway to the sublime. So, let us continue to unlock the secrets of the esoteric canvas, for in its enigmatic embrace, we discover the boundless potential of the human spirit.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Characteristics of Esoteric Art Styles?
Esoteric art is typified by the presence of symbolic imagery that alludes to mystical, spiritual, or occult themes. These styles can merge the abstract with the figurative to render the invisible and internal experiences tangible. They might also disrupt conventional perspectives to challenge the viewer’s understanding of reality.
How Do Artists Incorporate Esoteric Symbolism into Their Pieces?
Artists incorporate esoteric symbolism through the deliberate use of motifs and icons that have specific meanings within various mystical or arcane traditions. Symbols are often layered and interwoven with other elements in the art to convey complex spiritual narratives or to invoke introspection. In some instances, the inclusion of alchemical, astrological, or mythological references serve as a bridge to the esoteric content.
Isabella studied at the University of Cape Town in South Africa and graduated with a Bachelor of Arts majoring in English Literature & Language and Psychology. Throughout her undergraduate years, she took Art History as an additional subject and absolutely loved it. Building on from her art history knowledge that began in high school, art has always been a particular area of fascination for her. From learning about artworks previously unknown to her, or sharpening her existing understanding of specific works, the ability to continue learning within this interesting sphere excites her greatly.
Her focal points of interest in art history encompass profiling specific artists and art movements, as it is these areas where she is able to really dig deep into the rich narrative of the art world. Additionally, she particularly enjoys exploring the different artistic styles of the 20th century, as well as the important impact that female artists have had on the development of art history.
Learn more about Isabella Meyer and the Art in Context Team.
Cite this Article
Isabella, Meyer, “Esoteric Art – The World of Mystery and Symbolism.” Art in Context. March 6, 2024. URL: https://artincontext.org/esoteric-art/
Meyer, I. (2024, 6 March). Esoteric Art – The World of Mystery and Symbolism. Art in Context. https://artincontext.org/esoteric-art/
Meyer, Isabella. “Esoteric Art – The World of Mystery and Symbolism.” Art in Context, March 6, 2024. https://artincontext.org/esoteric-art/.