Harmony in Art – Looking at Different Examples of Harmony in Art
Have you ever viewed a painting and thought that it was almost near to perfect, there was just something to it that made it feel complete? This is probably because of the complimenting art elements creating harmony. But what is harmony in art exactly? In this article, we will delve deeper into finding a harmony in art definition, discussing its role as one of the principles of art as well as providing illustrative art and harmony painting examples.
Table of Contents
What Is Harmony in Art?
Harmony is one of the principles of art. These are utilized alongside the seven elements of art, which are the tools used to make an artwork, visually and contextually. The main principles of art are balance, emphasis, scale, proportion, movement, rhythm, variety, contrast, unity, and harmony.
The elements of art, which are also referred to as the “building blocks” of artwork are color, line, texture, value, space, shape, and form.
Harmony in art is created when these elements are utilized in such a way that they complement or relate to one another, for example, when similar color schemes are used, or the same shapes or forms are combined.

One art element can also be applied in a repeated manner among different art elements, which will still give the artwork a sense of harmony, such as if the same texture is utilized but there are different colors and shapes. We will discuss this further below. When there is a relation of art elements the art composition appears visually pleasing, or appealing, and it will be easier on our gaze.
However, it is also important to note the opposite of harmony is variety; when there is too much harmony and not enough variety, the artwork will potentially appear monotonous or uneventful.
The Difference Between Harmony and Unity
Before we move on, it is important to outline the differences between harmony and unity, as these two principles can be confused with each other because they are similar concepts. When it comes to harmony in art, it refers to various art elements arranged in relation to one another that makes the composition appealing and well-balanced, so to say.

Unity in art, on the other hand, refers to the overall holistic quality of an art composition, to which harmony will contribute. In fact, most of the principles of art will contribute to the overall unity of artwork, and how they are utilized will determine the level of unity. Unity is often described in terms of all the parts working “together”, giving the artwork “oneness”.
There are several techniques or methods that will aid in creating unity in an artwork, namely, proximity, repetition, and simplicity.
How to Create Harmony in Art
Creating harmony in art relates to all the elements in art working together or in effective relation to one another. Below, we will outline how important art elements like color, value, shape, form, and texture, can be utilized to create harmony in art.

Harmony Created by Color and Value
Harmony in color can be achieved through the minimal use of colors and not too many opposing colors. Utilizing different shades or tones of one color will create varying effects depending on the meaning of the subject matter; it can either create a sense of calm or be energized and lively, overall creating a unity of the whole.
There are also different color schemes to work with.
With the color wheel in mind, these are in different groups, namely, monochromatic; complementary, which are colors that occur opposite each other; analogous colors, which are colors next to each other; and triadic colors, which are three colors with even spaces between them.

An example of harmony in art using color includes Claude Monet’s Bridge Over a Pond of Water Lilies (1899), which depicts a dominance of blues and greens in softened tones, making it easy on our gaze. Another example includes Vincent van Gogh’s Quinces, lemons, pears and grapes (1887-1888), which is primarily painted with yellow with red shading here and there.
Harmony is created here because of the different tones of yellows, seemingly unifying all the other elements.

Harmony in value can be closely related to color, however, value in art refers to the lightness and darkness of a color. This is also better illustrated when a painting is viewed on a grayscale, which indicates darker or lighter areas.
This is what the value of the color is.
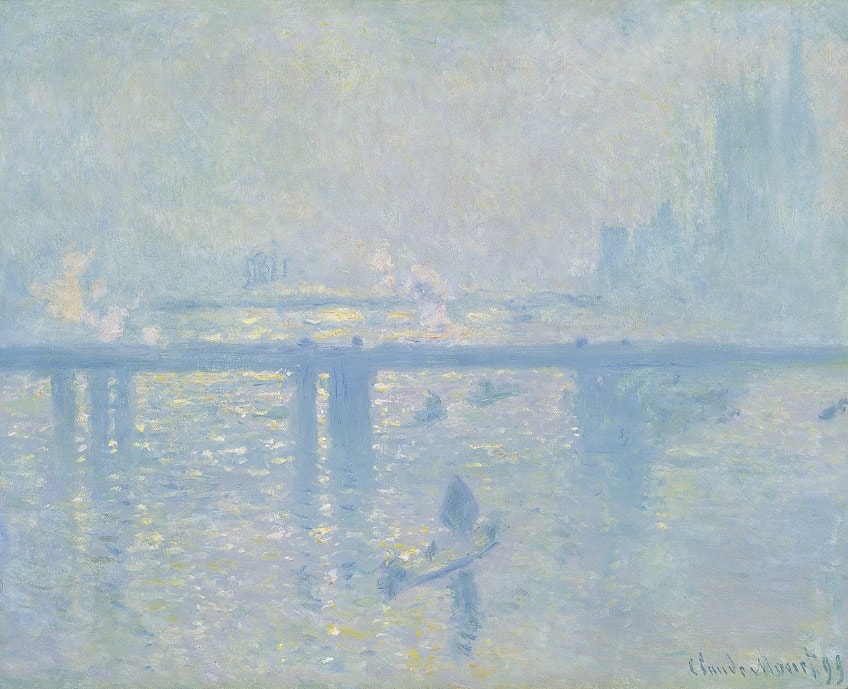
Examples of harmony in art using value include, again, another painting by Claude Monet, titled Charing Cross Bridge (1903). This illustrates what is known as a “high key” color value when lighter color tones are used; a “low key” color value refers to darker color tones, for example, Whistler’s Mother (1871) by James Abbot McNeill Whistler.
Harmony Created by Shapes and Forms
When similar shapes or forms are utilized in patterns or repetitions it creates a sense of consistency throughout the composition, which ultimately creates a sense of harmony. There are different shapes like circles, squares, rectangles, or triangles.
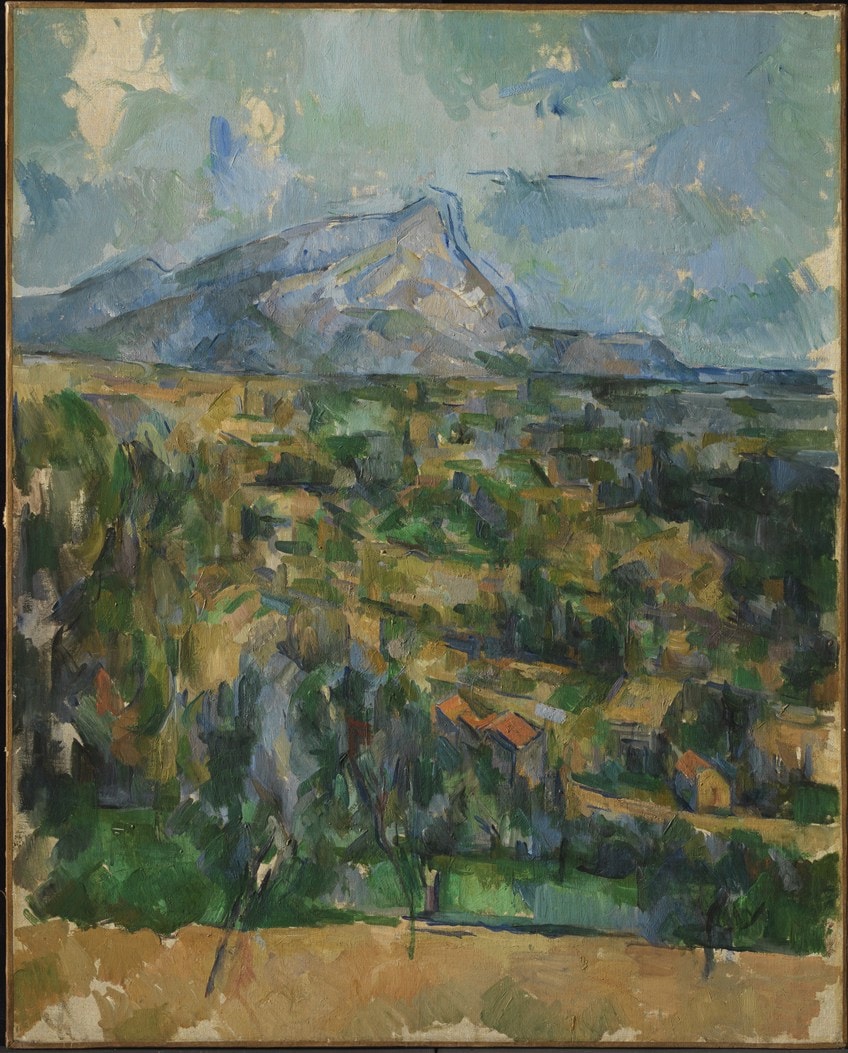
Examples of harmony in art using shapes include Paul Cézanne’s Mont Sainte-Victoire (1904-1906), which is composed of geometric structures illustrating the landscape, from the trees in the foreground to the houses in the middle-ground, and the angularity of the mountain in the background.
Although there is a strong dominance of shapes in this painting, it does not appear overly monotonous.

Many abstract artists utilize geometric shapes and forms to convey deeper meanings of life while some merely do it for no subjective meaning at all. If we look at Piet Mondrian’s Composition with grid #1 (1918), it depicts yellow, white, and gray squares and rectangles separated by thick black outlines.
Although the shapes are different in size, they are similar types, coupled with the minimal use of colors, giving the composition a congruency throughout.
Harmony and Texture
Texture in art is created by brushstrokes; if there is a consistent brushstroke style applied in a visual composition it can give it a sense of harmony due to the rhythm or flow the strokes follow. These can be even over the surface of the canvas, such as in watercolors or oil paintings, typically from Academic art where paintings followed strict rules of application, or it can be more haphazard and thicker, like the impasto technique, which is commonly seen in Impressionist paintings.
Famous examples of harmony in art using texture include Vincent van Gogh’s paintings like Olive Trees Under a Yellow Sky, and the November Sun (1889), which has a rhythmic flow of short, almost choppy, brushstrokes all over making up the subject matter.

Artists like Georges Seurat used another type of brushstroke referred to as Pointillism, which consisted of dots of paint. His A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte (1884-1886) is a famous example of this style, but also how the use of the same brushstroke style creates harmony even when different colors or shapes are utilized.
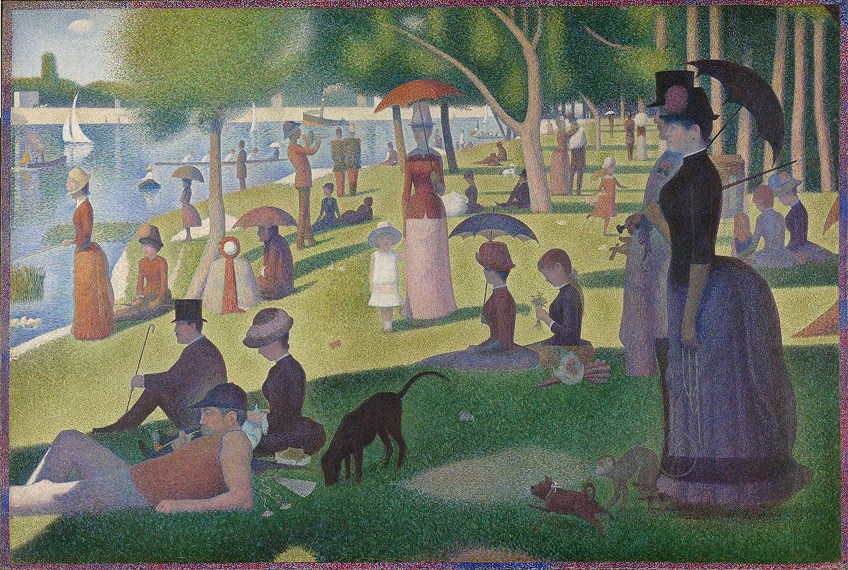
Summary of Harmony in Art
| Harmony in Art | Characteristics | Artwork Examples |
| Color and Value | Using different color schemes like monochromatic, complementary, analogous, and triadic colors. Using low-key or high-key color tones. | Bridge Over a Pond of Water Lilies (1899) by Claude Monet Quinces, lemons, pears and grapes (1887) by Vincent van Gogh Charing Cross Bridge (1903) by Claude Monet Whistler’s Mother (1871) by James Abbot McNeill Whistler |
| Shapes and Forms | Using similar geometric shapes or forms arranged in patterns or repeated. | Mont Sainte-Victoire (1904-1906) by Paul Cézanne Composition with grid #1 (1918) by Piet Mondrian |
| Texture | Using different types of textures like thick (Impasto) or thin, short, and long brushstrokes, applied evenly or haphazardly on the visual surface. | Olive Trees Under a Yellow Sky, and the November Sun (1889) by Vincent van Gogh Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte (1884) by Georges Seurat |
Principles of Art – Further Readings
- Principles of Art main article
- Movement in Art
- Emphasis in Art
- Unity in Art
- Rhythm in Art
- Texture in Art
- Proportion in Art
- Balance in Art
Towards uncovering the harmony in art definition, this article explored how it can be created through various art elements like color, value, shape, form, and texture. We also explored art and harmony painting examples, illustrating the different ways art elements can be applied to create a harmonious effect. There is no one-size-fits-all technique when it comes to harmony in art, and it requires a level of exploration to achieve the desired result. Each art element brings with it a unique style and when this is utilized with the principles of art, we can compose almost any visual artwork we wish to.
Take a look at our harmony art webstory here!
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Harmony in Art?
Harmony in art is when related or similar art elements are combined to create a so-called visually appealing artwork. Combined with the principles of art, this can be related to colors arranged in patterns or repetitions, or the same type of shapes or lines arranged in a way that creates rhythm, which results in a harmonious effect.
What Is the Difference Between Harmony and Unity in Art?
Harmony is about applying similar or repeated art elements to create an artwork that appears well-balanced or pleasing in a visual sense. Unity in art refers to the overall or broader idea of the artwork appearing visually pleasing, where all art elements work in unison.
What Are the Principles of Art?
The principles of art include harmony, balance, unity, proportion, scale, rhythm, movement, emphasis, variety, and contrast. These are also referred to as design principles and can be applied in all art modalities like painting, sculpture, graphic arts, or drawing, among others.
Alicia du Plessis is a multidisciplinary writer. She completed her Bachelor of Arts degree, majoring in Art History and Classical Civilization, as well as two Honors, namely, in Art History and Education and Development, at the University of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. For her main Honors project in Art History, she explored perceptions of the San Bushmen’s identity and the concept of the “Other”. She has also looked at the use of photography in art and how it has been used to portray people’s lives.
Alicia’s other areas of interest in Art History include the process of writing about Art History and how to analyze paintings. Some of her favorite art movements include Impressionism and German Expressionism. She is yet to complete her Masters in Art History (she would like to do this abroad in Europe) having given it some time to first develop more professional experience with the interest to one day lecture it too.
Alicia has been working for artincontext.com since 2021 as an author and art history expert. She has specialized in painting analysis and is covering most of our painting analysis.
Learn more about Alicia du Plessis and the Art in Context Team.
Cite this Article
Alicia, du Plessis, “Harmony in Art – Looking at Different Examples of Harmony in Art.” Art in Context. March 23, 2022. URL: https://artincontext.org/harmony-in-art/
du Plessis, A. (2022, 23 March). Harmony in Art – Looking at Different Examples of Harmony in Art. Art in Context. https://artincontext.org/harmony-in-art/
du Plessis, Alicia. “Harmony in Art – Looking at Different Examples of Harmony in Art.” Art in Context, March 23, 2022. https://artincontext.org/harmony-in-art/.











