Facts About Leonardo da Vinci – The Ultimate Renaissance Man
Leonardo da Vinci, often hailed as the quintessential Renaissance man, continues to fascinate and inspire us centuries after his time. Beyond his iconic paintings like the enigmatic Mona Lisa and the timeless The Last Supper, da Vinci’s genius spanned various fields, from anatomy and engineering to music and cartography. His insatiable curiosity led him to explore the mysteries of nature, leaving behind a legacy of innovation and creativity that transcends generations. Join us as we delve into lesser-known facts about this polymathic genius, unraveling the layers of his life and uncovering the secrets behind his enduring influence on art and science.
Table of Contents
- 1 The Legacy of Leonardo da Vinci
- 2 10 Interesting Facts About Leonardo da Vinci
- 2.1 His Name Was Not Really “Leonardo da Vinci”
- 2.2 Da Vinci Didn’t Go to School
- 2.3 His First Commissions Were Never Completed
- 2.4 He Wrote in Reverse
- 2.5 Da Vinci Didn’t Paint That Much
- 2.6 Da Vinci Was a Chronic Procrastinator
- 2.7 He Was an Accomplished Musician
- 2.8 Da Vinci’s Greatest Work Was Ruined by War
- 2.9 His Ideas Had Little Influence During the Period
- 2.10 He Was Fascinated by the Human Body
- 3 Frequently Asked Questions
The Legacy of Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo da Vinci’s legacy is nothing short of monumental, spanning across art, science, engineering, and philosophy. His pioneering spirit and relentless curiosity laid the groundwork for future generations of artists and thinkers, inspiring countless innovations and discoveries. From his revolutionary anatomical studies that advanced medical knowledge to his visionary designs for machines centuries ahead of their time, da Vinci’s legacy continues to shape our understanding of the world and our place in it.
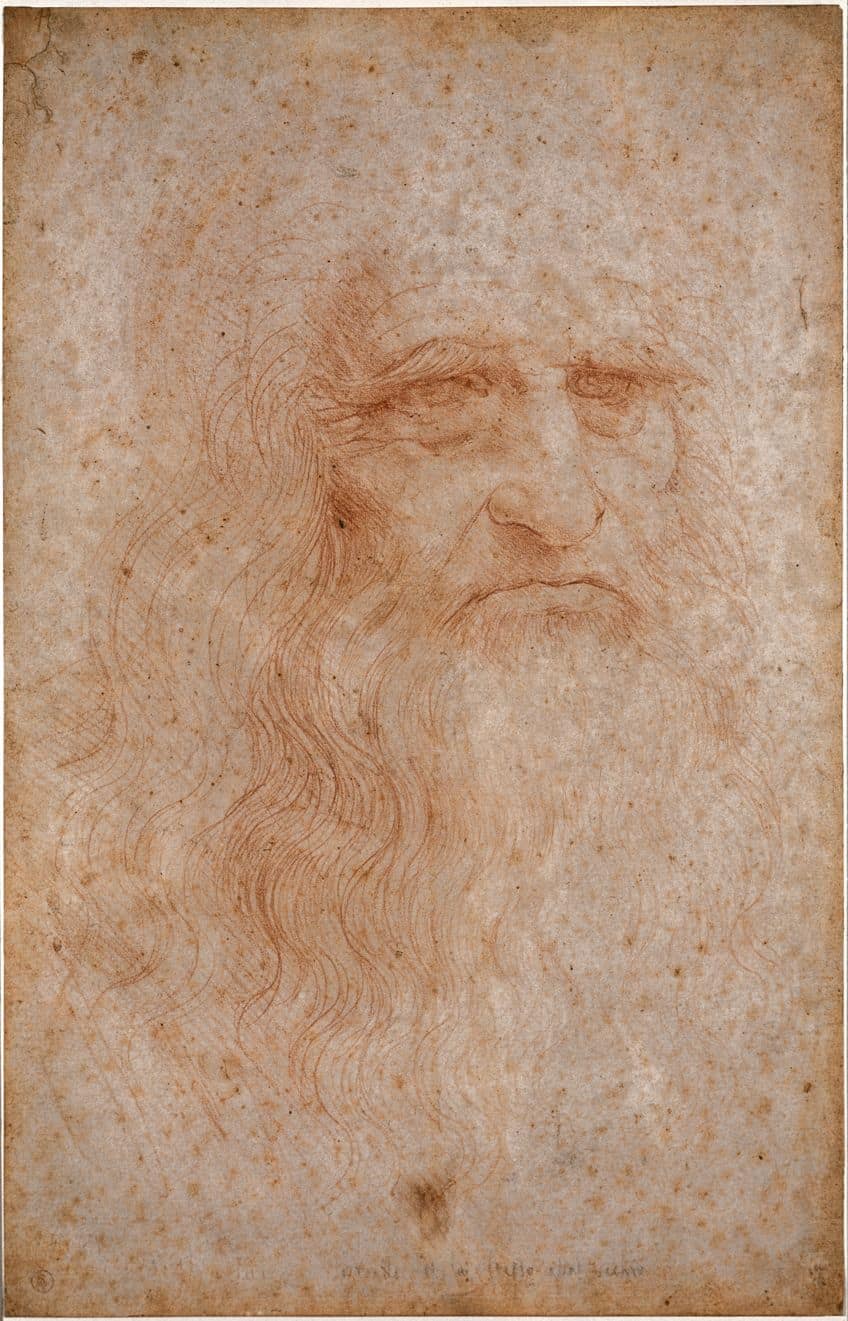

His masterpieces, like the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper, are not just timeless works of art but windows into a mind that sought to unravel the mysteries of existence. Beyond his artistic prowess, da Vinci’s legacy lies in his relentless pursuit of knowledge and his belief in the interconnectedness of all disciplines—a legacy that continues to inspire and captivate minds around the globe.
10 Interesting Facts About Leonardo da Vinci
In this section, we delve into fascinating facts about Leonardo da Vinci, the polymathic genius whose legacy continues to inspire awe and admiration centuries after his time. Beyond his renowned artistic masterpieces, da Vinci’s life is filled with intriguing details that illuminate his multifaceted talents, unorthodox habits, and enduring impact on art, science, and humanity.
From his unconventional approach to education and work habits to his deep fascination with the mysteries of the human body and the complexities of war, these facts offer a glimpse into the extraordinary mind of one of history’s most celebrated figures.
His Name Was Not Really “Leonardo da Vinci”
The term “da Vinci” means “of Vinci,” indicating Leonardo’s birthplace rather than a surname. In Renaissance Italy, people were often identified by their birthplaces, and Vinci was where Leonardo was born in 1452. This naming convention was typical for the era, reflecting a person’s origin rather than a family name.

Da Vinci Didn’t Go to School
Leonardo’s lack of formal schooling was not uncommon for the period, especially among those pursuing artistic or artisanal careers. Instead, he received an apprenticeship in Verrocchio’s workshop, where he learned painting, sculpting, and other artistic techniques alongside practical skills like drafting and metalworking.
This hands-on training shaped his multifaceted talents and innovative approach to art and science.
His First Commissions Were Never Completed
Leonardo’s early commissions, such as The Adoration of the Magi for the Monastery of San Donato a Scopeto and The Battle of Anghiari for the Palazzo Vecchio in Florence, remained unfinished. His tendency to explore diverse interests and his perfectionist nature often led him to abandon projects or delay their completion, focusing instead on experimentation and continuous learning.
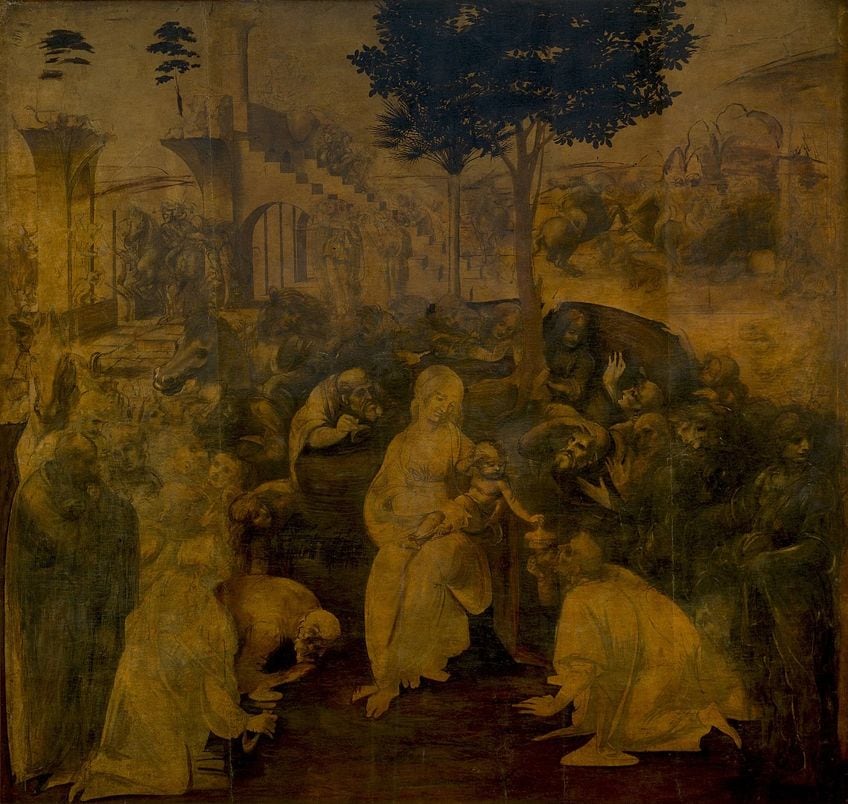

He Wrote in Reverse
Leonardo’s use of mirror writing, where letters are reversed and written from right to left, has puzzled historians and scholars. Some speculate that it was a practical measure to prevent smudging while writing with ink and quill, as Leonardo was left-handed. Others suggest that it was a way to protect his ideas and notes from casual readers, requiring a mirror to decipher his writings accurately.
This unique writing style adds to the enigmatic allure of Leonardo da Vinci’s personality and legacy.
Da Vinci Didn’t Paint That Much
Despite his reputation as a painter, Leonardo’s output in this medium was relatively limited. This was partly due to his meticulous approach, which involved extensive preparatory studies and research before executing a painting. Additionally, his diverse interests in anatomy, engineering, and natural phenomena often diverted his attention from painting, leading him to prioritize scientific inquiry alongside his artistic endeavors.
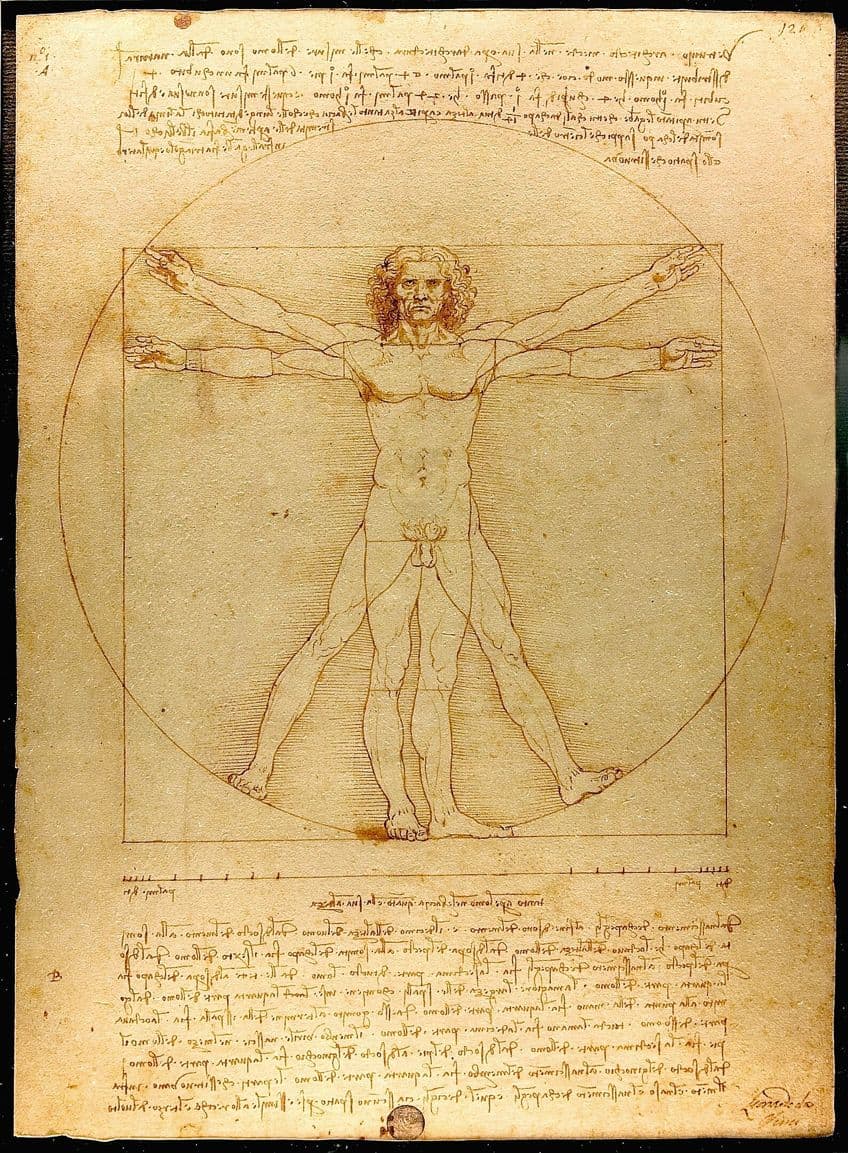
Da Vinci Was a Chronic Procrastinator
Leonardo’s tendency to procrastinate stemmed from his perfectionism and insatiable curiosity. He often became engrossed in multiple projects simultaneously, exploring diverse subjects from anatomy and engineering to botany and architecture.
This multitasking approach, while indicative of his genius, sometimes led to delays in completing his works.
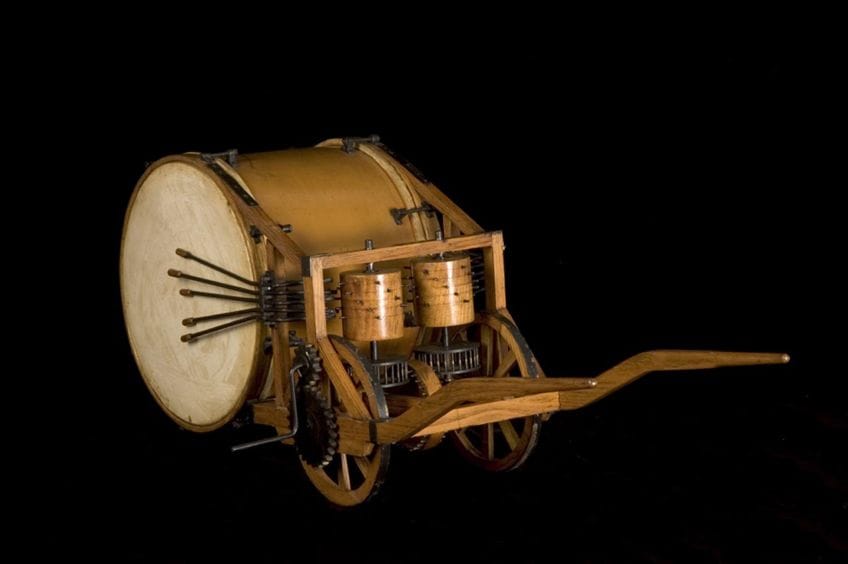
He Was an Accomplished Musician
Leonardo da Vinci’s musical talents were notable among his peers. He not only played instruments but also composed music. His interest in music extended to designing instruments and studying the mathematical principles behind musical harmony, reflecting his holistic approach to art and science.

Da Vinci’s Greatest Work Was Ruined by War
The Battle of Anghiari mural, considered one of Leonardo’s masterpieces, was never completed due to external circumstances. War and political upheaval disrupted the project, leading to the eventual loss of the original artwork.
However, its innovative techniques and artistic vision influenced later generations of artists and historians, making it a symbol of both artistic ambition and historical contingency.
His Ideas Had Little Influence During the Period
Despite his visionary ideas, Leonardo faced challenges in disseminating his work widely during his lifetime. The slow pace of communication and limited access to his notebooks meant that many of his groundbreaking concepts, such as flying machines and hydraulic engineering designs, had little immediate impact on contemporary society.
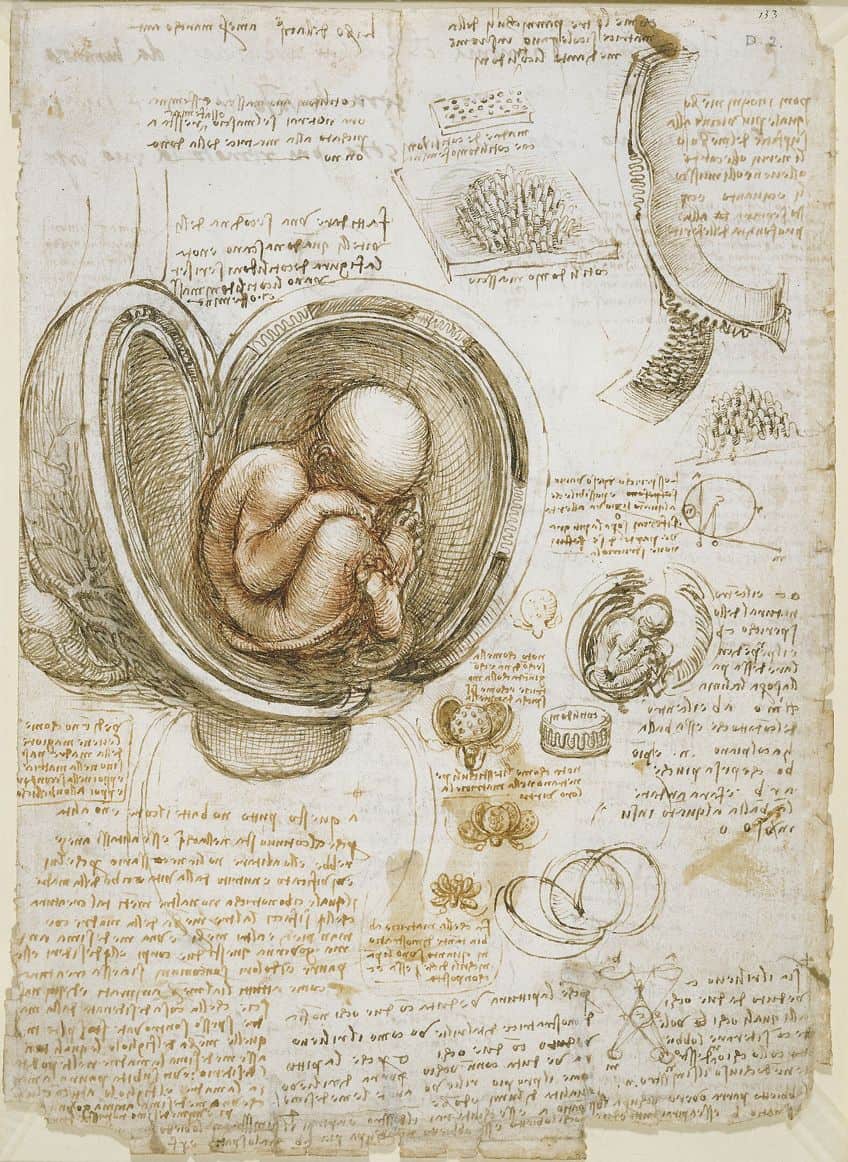
He Was Fascinated by the Human Body
Leonardo’s anatomical studies went beyond artistic representation; they were scientific inquiries into the functioning of the human body. His dissections and detailed drawings revealed insights into anatomy that were ahead of his time, laying the foundation for modern medical illustration and understanding.
Leonardo da Vinci’s life and works are a testament to the boundless possibilities of human imagination and ingenuity. From his revolutionary studies of human anatomy to his intricate designs for flying machines, da Vinci’s legacy is a testament to the power of interdisciplinary thinking and relentless curiosity. As we reflect on the lesser-known facets of his life, we are reminded of the timeless relevance of his ideas and the profound impact he has had on art, science, and the very essence of what it means to be a Renaissance thinker. Leonardo da Vinci remains a beacon of inspiration, challenging us to push the boundaries of knowledge and creativity, inviting us to explore the uncharted territories of our own potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Many Paintings Did Leonardo da Vinci Complete in His Lifetime?
Leonardo da Vinci completed only around 15 paintings that are attributed to him today. His meticulous approach and diverse interests often led him to spend more time on scientific studies and inventions than on painting.
What Was Leonardo da Vinci’s Fascination With Anatomy?
Leonardo da Vinci’s fascination with anatomy stemmed from his desire to understand the human body’s inner workings. He conducted meticulous dissections and made detailed anatomical drawings, contributing significantly to medical knowledge and artistic representation.
How Did Leonardo da Vinci’s Ideas and Inventions Influence Future Generations?
Leonardo da Vinci’s ideas and inventions had a profound impact on subsequent generations, shaping fields such as art, engineering, anatomy, and scientific inquiry. His visionary concepts continue to inspire creativity and innovation today.
Isabella studied at the University of Cape Town in South Africa and graduated with a Bachelor of Arts majoring in English Literature & Language and Psychology. Throughout her undergraduate years, she took Art History as an additional subject and absolutely loved it. Building on from her art history knowledge that began in high school, art has always been a particular area of fascination for her. From learning about artworks previously unknown to her, or sharpening her existing understanding of specific works, the ability to continue learning within this interesting sphere excites her greatly.
Her focal points of interest in art history encompass profiling specific artists and art movements, as it is these areas where she is able to really dig deep into the rich narrative of the art world. Additionally, she particularly enjoys exploring the different artistic styles of the 20th century, as well as the important impact that female artists have had on the development of art history.
Learn more about Isabella Meyer and the Art in Context Team.
Cite this Article
Isabella, Meyer, “Facts About Leonardo da Vinci – The Ultimate Renaissance Man.” Art in Context. April 10, 2024. URL: https://artincontext.org/facts-about-leonardo-da-vinci/
Meyer, I. (2024, 10 April). Facts About Leonardo da Vinci – The Ultimate Renaissance Man. Art in Context. https://artincontext.org/facts-about-leonardo-da-vinci/
Meyer, Isabella. “Facts About Leonardo da Vinci – The Ultimate Renaissance Man.” Art in Context, April 10, 2024. https://artincontext.org/facts-about-leonardo-da-vinci/.











