“The Intervention of the Sabine Women” – By Jacques-Louis David
Step into the tumultuous world of Jacques-Louis David’s masterpiece, The Intervention of the Sabine Women, where passion clashes with politics, and history unfolds in strokes of grandeur. Picture this: Rome, in the throes of conflict, where the bold brush of David captures a moment of both chaos and harmony. As the Sabine women rush to reconcile warring factions, the canvas ignites with emotion, inviting us to ponder the power of love, diplomacy, and artistic mastery. Join us on a journey through this iconic painting, where each stroke whispers secrets of antiquity and each figure tells a story of courage and reconciliation.
Table of Contents
Key Takeaways
- Jacques-Louis David’s The Intervention of the Sabine Women is a significant Neoclassical painting housed at the Louvre.
- The artwork captures a mythological moment infused with the political sentiment of 18th-century France.
- David’s use of composition and color in the painting exemplifies his expertise and contributes to the work’s enduring legacy in art history.
Historical Context
| Artist | Jacques-Louis David (1748 – 1825) |
| Date Created | 1799 |
| Medium | Oil on canvas |
| Genre | History painting, Neoclassicism |
| Period/Movement | Neoclassical |
| Dimensions (cm) | 385 x 522 |
| Series/Versions | Single version, no known series |
| Where Is It Housed? | Louvre Museum, Paris, France |
| What It Is Worth | Priceless, considered a national treasure, not for sale |
The Intervention of the Sabine Women is a seminal work of art by Jacques-Louis David, a leading figure in French Neoclassical painting. Completed in 1799, this arresting oil on canvas depicts a dramatic moment from the early history of Rome. The narrative, derived from ancient mythology, showcases the Sabine women intervening to stop a battle between their former Roman captors and their Sabine families.
The painting is revered not only for its compelling interpretation of the legendary event but also for how it reflects the political and social climate of France during the time of its creation.
Jacques-Louis David’s masterpiece is housed in the Musée du Louvre in Paris, where it stands as a testament to his skill in portraying historical narratives with emotional depth and political nuance. With a canvas that stretches over 3 meters tall and 5 meters wide, the work’s scale adds to its dramatic impact. The powerful use of composition, lighting, and color underlines David’s mastery and his capacity to express complex themes through his work.

This painting, by one of the foremost artists of his era, encapsulates the Neoclassical ideal and continues to influence discussions in art and history. The Intervention of the Sabine Women is deeply rooted in ancient legend and political undertones from the time of the French Revolution. This historical canvas mirrors both the mythological and socio-political narratives that were influential during David’s life.
The Sabine Legend and Its Influence
The narrative depicted by David is derived from the legendary episode concerning the founding generation of Rome. According to the legend, Romulus, the founder of Rome, faced a shortage of women for his male citizens. To rectify this, Romulus invited neighboring Sabine families to a festival and, at a predetermined signal, the Roman men abducted the Sabine women to take as wives.
This act, known as the “Rape of the Sabine Women,” was later followed by a dramatic intervention where the women, having integrated into Roman society, intervened to stop a battle between their Roman husbands and Sabine relatives.
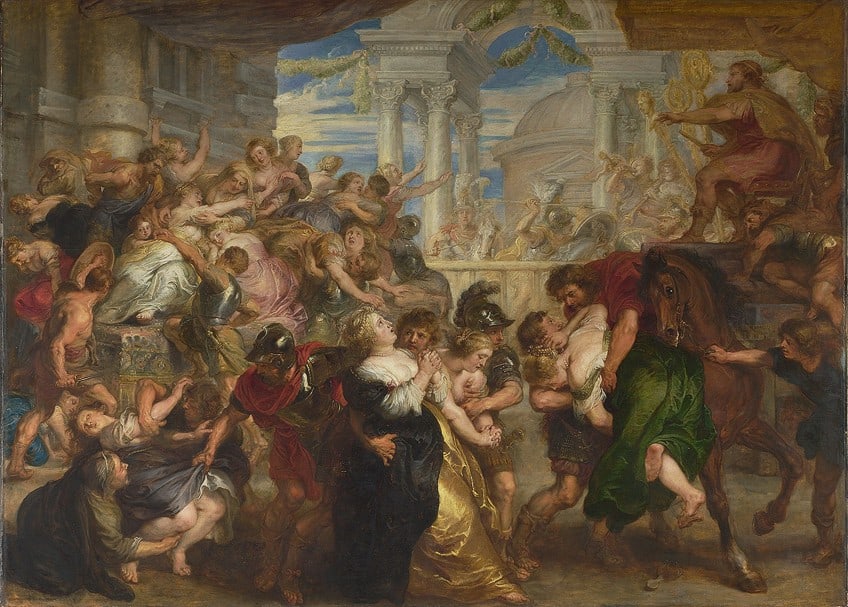

Jacques-Louis David chose to capture the moment of intervention, which emphasized reconciliation and peace. The Sabine women are depicted as pivotal figures who halted conflict, thus symbolizing a powerful narrative of unity and resolution that contrasted sharply with the political discord of David’s own times.
Neoclassicism and Revolution
David, an ardent supporter of the French Revolution, was acutely influenced by the Neoclassical style, which sought to emulate the arts of classical antiquity. His art often portrayed themes from classical history and mythology, which resonated with contemporary revolutionary ideals such as republicanism, virtue, and citizenry. The Intervention of the Sabine Women, completed during the Thermidorian Reaction—a period of relative calm following the Reign of Terror—reflects the societal yearning for stability and moderation.
While the painting was created during a politically turbulent period in Europe, as nations grappled with the effects of the French Revolution and the rise of Napoleon, it was intended to be displayed in the Luxembourg Palace.
However, it was ultimately placed in the Louvre Museum, becoming accessible to a wider audience. David’s portrayal of classical themes interpreted within the context of revolutionary fervor was a testament to the complex interplay between European nations and their engagement with cultural and political transformation.
Formal Analysis
This section of the article provides a detailed formal analysis of Jacques-Louis David’s painting The Intervention of the Sabine Women, covering key aspects such as subject matter, symbolism, composition, technique, and interpretation.

Subject Matter
The painting depicts a dramatic scene from Roman mythology. The Sabine women are intervening to stop a battle between their Sabine families and their Roman captors, represented by the central female figure, Hersilia, as she intervenes between her husband, Romulus, the founder of Rome, and her father, the Sabine king Titus Tatius.
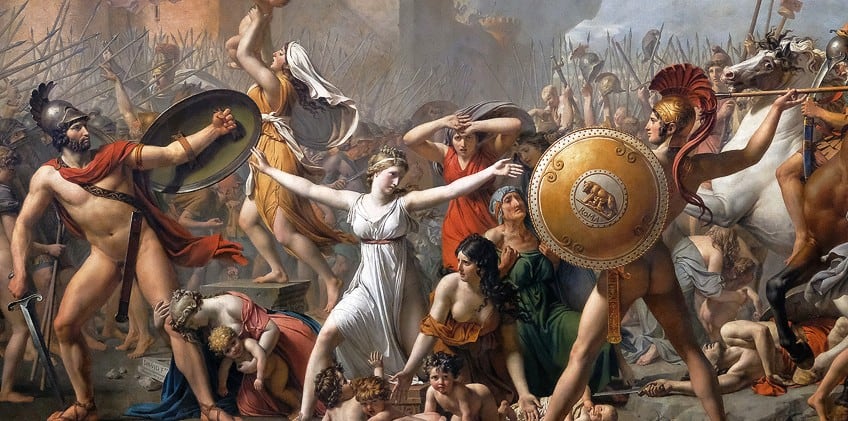
Symbolism and Themes
Hersilia functions as a symbol of peace and unity, her outstretched arms bridging the divide between opposing sides. The work explores themes of conflict, reconciliation, and the role of women in society.
The Intervention of the Sabine Women encapsulates themes of reconciliation, peace, and the transformative power of human agency, while also reflecting the political and social dynamics of its time.
- Unity and reconciliation: At its core, the painting symbolizes the reconciliation between conflicting parties. The gesture of the central female figure, intervening to halt the battle between Romans and Sabines, represents the power of unity and diplomacy over conflict and division.
- Peace and harmony: The scene captures a moment of transition from chaos to order, as peace emerges from the tumult of warfare. The outstretched arms of the women and the subdued expressions of the men convey a desire for peace and reconciliation.
- Neoclassical ideals: As a quintessential work of Neoclassicism, the painting embodies the ideals of ancient Greece and Rome, emphasizing order, rationality, and idealized forms. The architectural elements in the background evoke the grandeur of classical antiquity, reinforcing the theme of civic virtue and moral integrity.
- Female agency: The central role of women in resolving the conflict highlights the agency and influence of women in shaping historical events. The Sabine women assert their authority and demand recognition as active participants in the political and social life of ancient Rome.
- Political allegory: Against the backdrop of revolutionary France, David’s painting served as a political allegory, advocating for reconciliation and unity amidst the chaos of revolution. The theme of fraternity and the pursuit of common goals resonated with the ideals of the French Revolution, where the nation sought to overcome divisions and establish a new order based on principles of liberty and equality.
Composition and Technique
David employs a neoclassical style, characterized by clarity, order, and harmony. The composition is focused on the triangular arrangement of key figures, with Hersilia at the apex. The use of chiaroscuro highlights the central action, and the careful arrangement of figures leads the viewer’s eye throughout the painting.

- Use of space: Figures are arranged on parallel planes, providing depth.
- Color palette: Controlled and subdued, emphasizing the gravity of the scene.
- Brushwork: Precise and fine, typical of David’s commitment to polished surfaces.
Interpretation of Artwork
David’s painting is often interpreted as an allegory for political resolution, alluding to the potential for peace during a tumultuous period in France.
It reflects on the power of intervention and the possibility of ending conflict through courage and compassion.
Legacy of the Painting
The Intervention of the Sabine Women by Jacques-Louis David has solidified a substantial legacy in the art world due to its powerful representation of peace and reconciliation. The artwork is celebrated for its dramatic portrayal of a pivotal moment in Roman mythology where Sabine women intervene to prevent a conflict between their Roman husbands and Sabine brothers.
Exhibited prominently at the Louvre Museum in Paris, Jacques-Louis David’s The Intervention of the Sabine Women remains a captivating centerpiece, attracting numerous visitors annually.
Its neoclassical style and poignant political narrative have left an indelible mark on contemporary painters, influencing generations with its technical mastery and compelling storytelling. As scholars and enthusiasts continue to study its nuances, the painting stands as a testament to the enduring power of art to inspire, provoke thought, and shape cultural discourse.
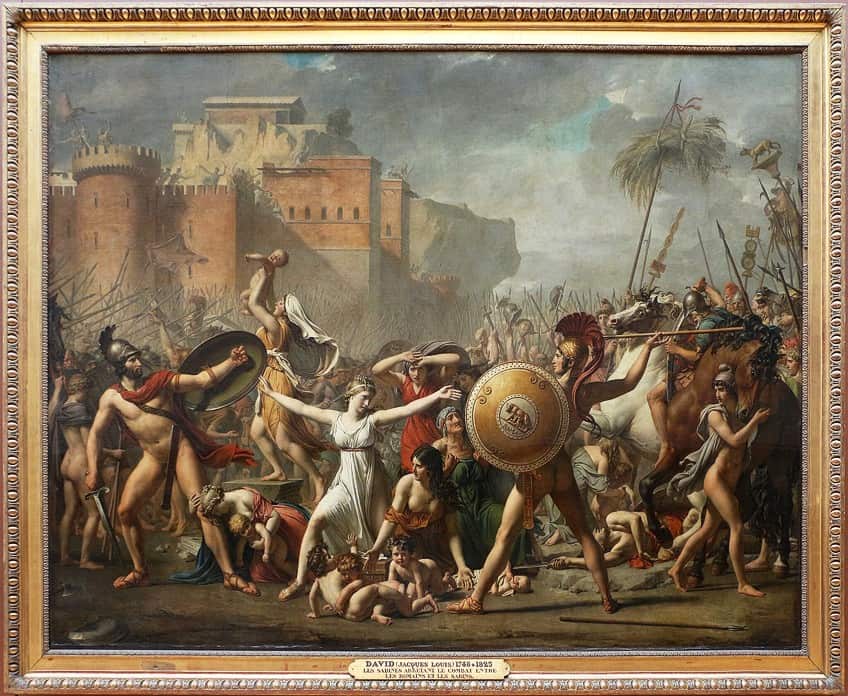

David’s composition garners praise for its masterful arrangement of figures and the astute utilization of space to convey the emotional intensity of the scene. Esteemed by art historians as an exemplar of neoclassical history painting, the work embodies the principles of the era with its precise lines, idealized forms, and dramatic narrative. As a pinnacle of artistic achievement, it continues to inspire and captivate audiences, inviting contemplation of its technical brilliance and enduring significance in the annals of art history.
The Intervention of the Sabine Women has sparked extensive discussions within academic circles, enriching discourse on themes of love, sacrifice, and the evolving role of women in society.
Its profound impact extends beyond artistic appreciation, frequently cited as a reference point in discussions about the intersection of politics and art. As a cultural touchstone, Jacques-Louis David’s masterpiece continues to resonate, prompting reflection on the enduring relevance of historical narratives and the power of visual storytelling to shape our understanding of the human experience.

The work is pivotal in art education, representing the shift to neoclassicism and the revival of classical themes in European art. It offers students insights into the movement’s aesthetic principles and historical context, serving as a key piece for exploring tradition, innovation, and cultural identity within Western art history. Through its exhibition, influence, and impact on culture and education, the painting’s legacy endures, underpinning its significance as a historical and artistic beacon.
As we bid adieu to the compelling tableau of The Intervention of the Sabine Women by Jacques-Louis David, we leave behind a world brimming with intrigue, passion, and the indomitable spirit of humanity. David’s brush immortalizes a moment of profound transformation, where conflict gives way to connection, and discord yields to harmony. As we reflect on the timeless allure of this masterpiece, let us remember that art not only mirrors history but also serves as a beacon of hope, reminding us of our capacity for empathy, understanding, and the triumph of the human spirit against the backdrop of tumultuous times. In the canvas of life, may we continue to find inspiration and enlightenment, much like the enduring legacy of The Intervention of the Sabine Women.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Historical Significance Behind The Intervention of the Sabine Women?
Jacques-Louis David’s painting portrays the legendary episode in Roman history where Romulus, the founder of Rome, and his followers sought wives by inviting neighboring Sabine tribes to a festival. However, during the festivities, the Romans abducted the Sabine women, leading to conflict. The painting captures the pivotal moment when the Sabine women intervene to halt the bloodshed and reconcile the warring factions.
How Does The Intervention of the Sabine Women Reflect the Political Climate of Its Time?
David created the painting during a period of political upheaval in France, where revolutionary ideals of liberty, equality, and fraternity were gaining momentum. The theme of reconciliation in the painting resonated with the political rhetoric of the time, serving as a metaphor for the need to unite and reconcile conflicting factions for the greater good of society.
How Did The Intervention of the Sabine Women Contribute to Jacques-Louis David’s Legacy as an Artist?
David’s painting not only solidified his reputation as one of the foremost Neoclassical painters but also cemented his role as a political artist who used his work to advocate for social change. The monumental scale and emotional resonance of The Intervention of the Sabine Women continue to captivate audiences, ensuring David’s enduring influence on the history of art.
Isabella studied at the University of Cape Town in South Africa and graduated with a Bachelor of Arts majoring in English Literature & Language and Psychology. Throughout her undergraduate years, she took Art History as an additional subject and absolutely loved it. Building on from her art history knowledge that began in high school, art has always been a particular area of fascination for her. From learning about artworks previously unknown to her, or sharpening her existing understanding of specific works, the ability to continue learning within this interesting sphere excites her greatly.
Her focal points of interest in art history encompass profiling specific artists and art movements, as it is these areas where she is able to really dig deep into the rich narrative of the art world. Additionally, she particularly enjoys exploring the different artistic styles of the 20th century, as well as the important impact that female artists have had on the development of art history.
Learn more about Isabella Meyer and the Art in Context Team.
Cite this Article
Isabella, Meyer, ““The Intervention of the Sabine Women” – By Jacques-Louis David.” Art in Context. February 28, 2024. URL: https://artincontext.org/the-intervention-of-the-sabine-women-by-jacques-louis-david/
Meyer, I. (2024, 28 February). “The Intervention of the Sabine Women” – By Jacques-Louis David. Art in Context. https://artincontext.org/the-intervention-of-the-sabine-women-by-jacques-louis-david/
Meyer, Isabella. ““The Intervention of the Sabine Women” – By Jacques-Louis David.” Art in Context, February 28, 2024. https://artincontext.org/the-intervention-of-the-sabine-women-by-jacques-louis-david/.











